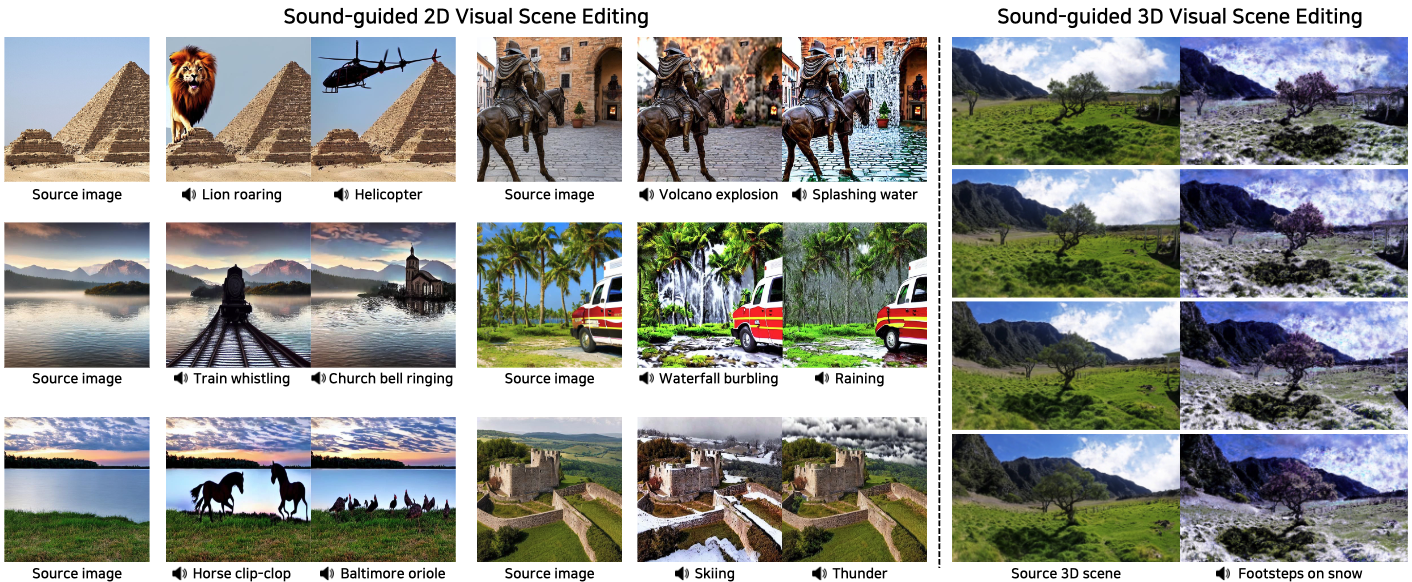
We propose SoundBrush, a model that uses sound as a brush to edit and manipulate visual scenes. We extend the generative capabilities of the Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) to incorporate audio information for editing visual scenes. Inspired by existing image-editing works, we frame this task as a supervised learning problem and leverage various off-the-shelf models to construct a sound-paired visual scene dataset for training. This richly generated dataset enables SoundBrush to learn to map audio features into the textual space of the LDM, allowing for visual scene editing guided by diverse in-the-wild sound. Unlike existing methods, SoundBrush can accurately manipulate the overall scenery or even insert sounding objects to best match the audio inputs while preserving the original content. Furthermore, by integrating with novel view synthesis techniques, our framework can be extended to edit 3D scenes, facilitating sound-driven 3D scene manipulation.
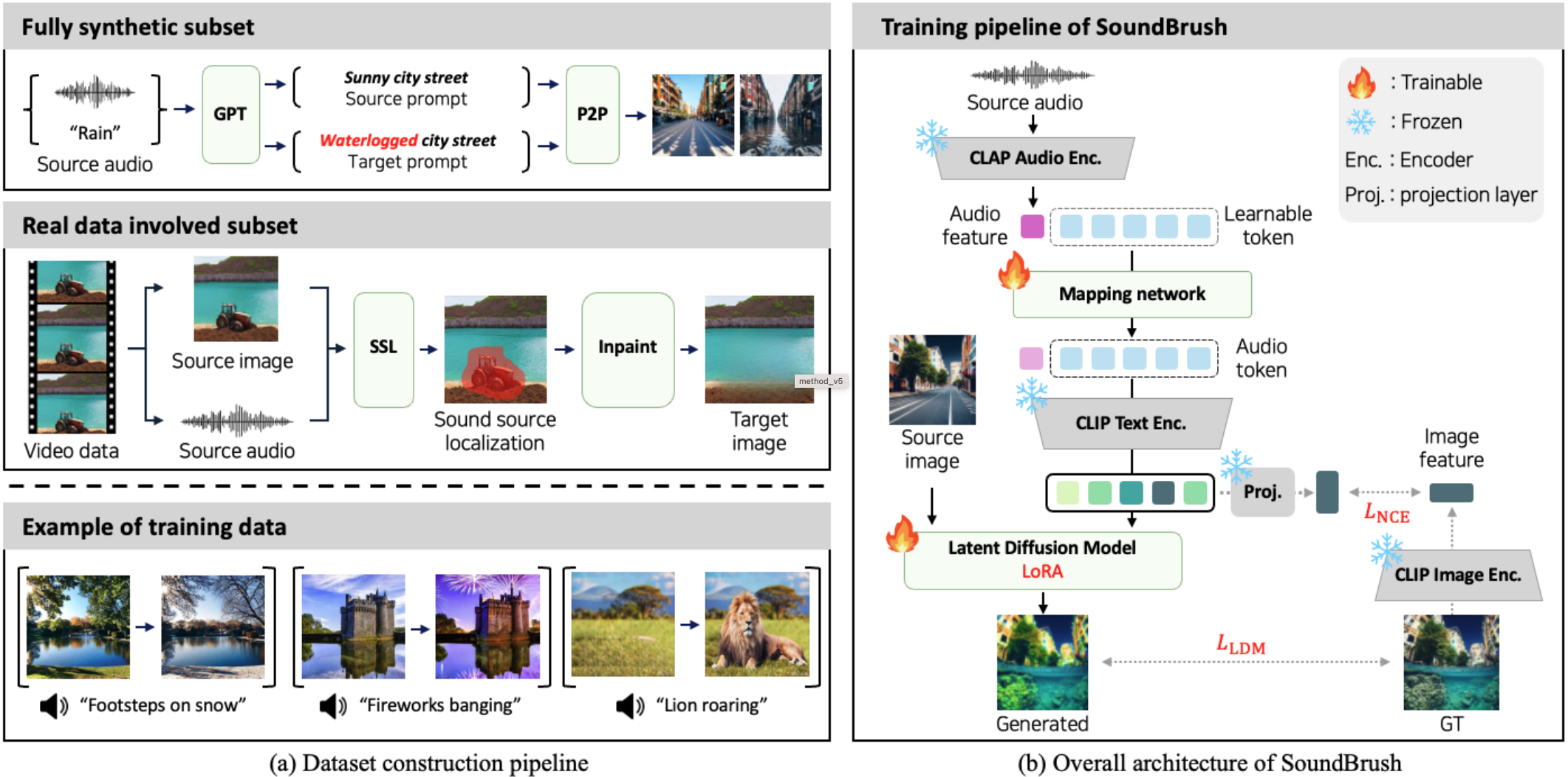
We start by designing an automatic dataset-construction pipeline as in (a). The dataset is constructed with a fully synthetic subset, involving synthetically generated image pairs paired with audio, and real data involved subset, involving real audio and images. Using this dataset, we train SoundBrush to learn to effectively translate the audio features into the audio tokens, so that these tokens can be used for control signal for image editing latent diffusion model as in (b).
|
Given Image |
Edited Images |
Given Image |
Edited Images |
||

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |
|
Original Video |
InstructAny2Pix |
SoundBrush(Ours) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
@inproceedings{soundbrush,
author = {Sung-Bin, Kim and Jun-Seong, Kim and Ko, Junseok and Kim, Yewon and Oh, Tae-Hyun},
title = {SoundBrush: Sound as a Brush for Visual Scene Editing},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
year = {2025}
}